The structure of the root. An online lesson
The roots of plants have two main functions: 1) fixing the plant in the soil, 2) the absorption of water and dissolved in it minerals. However, often roots of plants perform a number of additional functions, as a result of which they are modified, i.e., in nature there are radiation modifications.
Below are the most well-known radiation modifications.
Roots
Kornemploda is the modification of the main root and the lower part of the stem, in which spare nutrients (starch, sugar, etc.) accumulate. Roots are characteristic of plants such as beets and carrots, as well as a number of others.
Most often, rooted roots are found in bilateral plants. They are formed at the end of the first growing season of such a plant, usually at the end of the summer or early autumn. The plant for the summer accumulates spare nutrients, in the fall, its above-ground part is dying. In the second year in the spring, the stems and leaves grow again. In this case, spare substances from the root plant are used. At this year, the plant blooms and fruits, after which he dies completely.
Rights of many plants man uses for its power. The crop is collected in the first year. If you need to get seeds, the rootpode is left in the soil for the second year.
Root tubers
Root tubers are modifying the apparent and side roots in which spare nutrients accumulate. Tubers are characteristic of such plants as a batt, dahlias and a number of others.
Root tubers are differently called root cones.
Root trains
Root hooks (or root-hooks) is modifying the apparent roots that serve as a plant to attach to any support. These roots are above the soil. So the plant puts out its vegetative parts (stem and leaves) to the light in the absence of a solid stem. Root trains can be observed in ivy.
Root backpoints
Root backups, or support roots, are also developing from pressing roots and are in the air. They are formed in a number of tropical trees on the trunks and branches. Next they grow to the soil. At its surface, they are very branched and, as it should be supported by the plant. An example of a plant with backup roots is a banyan.
Air roots
Air roots are characteristic of orchids that grow on tropical trees. Here the roots of orchids just hang down. In tropical forests is very humid, so water can be absorbed directly from the air.
Root suckers
The roots of the suction cups can also be observed by the mistletoe, the rattles, Ivan-da-Marya. They suck only water and minerals.
Definition
Root - axial underground organ plant with unlimited terminal growth.
Types of roots (Fig. 1):
Main root It develops from the embryonic root of the seed and plays the role of the central axis of the underground part in the plant.
Putting roots Grow from escape.
Side roots They are formed on the main and apparent roots.
The whole totality of the roots of the plant is called root system.
types of root systems
Depending on the development of certain types of roots, two types of root systems are distinguished (Fig. 2).
Rod root system It consists of a well-developed main root and the smaller side roots departing from it, which in turn are divided into the lateral roots of the second, third, etc. of orders.
Such a root system is characteristic of dousegone plants and is well visible only in young plants grown from seeds. For old perennial plants, the main root slows down growth over time, and the side roots catch up with it or even develop.
Uriscouched root system consists of numerous pressing and side roots. The main root does not develop or develop weakly.
The urine root system is characteristic of monocotyledonic plants.

Fig. 2. Types of root systems
the inner structure of the root
The root is distinguished in the root of the root, each of which has a certain structure and performs certain functions (Fig. 3).
Seed zoneit consists of small constantly dividing cells of the elite meristem. This zone is on the tips of all roots of the plant. Due to the top meristem, the root growth is carried out.
Root case - Several layers of tightly contrived cells with thickened walls.
Root case function:
mechanical protection of the division zone;
selection of mucous meal for easier penetration into the soil.
Cells outside the root case are constantly destroyed, and on the inside it increases due to the cells of the meristem.
Picking root- Removal of the tip of the main root - is made to stop the growth of the main root and enhancing the growth of lateral roots: the total area of \u200b\u200broot food increases.

Fig. 3. Root zones
Stretching Zone (Growth). In it, the cells grow, stretching in length, due to which the root elongation occurs.
In the same area, cell differentiation begins. Surface cells are converted into cells rizoderma. Cells of conductive tissues are formed in the center.
Suction zone. Suction area outside covered with fine coat epiBleme(or Rizoderma). In this zone, epibloma cells form outgrowths - root hairs. Root hairs are long fine filamentous cellular growths in which the cell core moves. As the root increases, they are destroyed, the epiderm of the plug and the suction zone is replaced by the test area.
Function of root hairs: Absorption of water soil and minerals.
Zone holding It continues to land parts of the plant. It contains the vessels of Xilera, according to which water rises with minerals, and the coat tubes of the Floem, along which organic substances from the leaves come to the root.
Histological structure root
On the cross section of the young part (the top of the stretch zone), the root can be seen that the parenchymal cells of the cortex are most of its part (Fig. 4). From above, they are covered with single-layer epibloma, and in the middle there are primitives of xylems and flora. They are surrounded by two special cell layers: endoderma and pericycle.
Endoderma - the inner single-row layer of tightly closed cells of the primary cortex adjacent to the central cylinder of the axial organs of higher plants.
In the roots of the radial and transverse walls of the cells of the endoderma have thickening in the form of belt containing suburin and lignin (Kaspari's belts), thin-walled remain throughput cells of this layer. Thus, the endoderma is a physiological barrier regulating the flow of water and ions from the primary bark in the central cylinder of the root.
Pericycle or perikambiy - Primary educational fabric of plants surrounding conductive fabrics. Forms the axial cylinder, the outer layer of which it is. In it laid apparent and side roots. Didual schools differentiate in Cambier and fellogen. During the secondary rock thickening.
Fellogen,or Cork Cambier - educational fabric, giving the beginning of secondary coating fabric - cork.
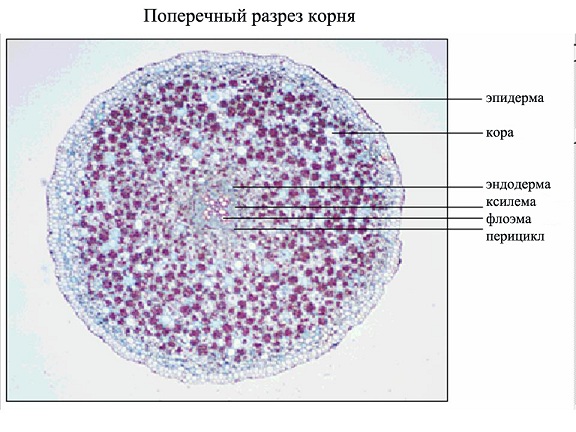
Fig. 4. Young root (cross-section)
In later stages, a conductive root system is formed (Fig. 5).

Fig. 5. Conductive root system
The surrounding system has a circle form on a cut, so it is often called conductive cylinder. Xilema is located in the center and forms the structure of the star with rays, reaching the edge of the conductive cylinder.
Floem is located in the intervals between the rays of Xleema.
There is a layer of Cambia between xylem and the Floem, which makes the formation of new conductive elements.
Endodermasurrounding the conductive cylinder plays the role of a locking mechanism. Its cells are tightly connected to each other, their walls are impregnated with waterproof substances, due to which water and mineral salts cannot exit the conductive cylinder of the lobby and are forced to move upwards. From the cells of the cortex, water and mineral salts fall into the conductive cylinder due to the presence in the ring of the Endoderma special bandwidths.
PericycleLocated under the endoderma, is an educational fabric that gives rise to side roots (Fig. 6).

Fig. 6. Education pericycle side roots
As a result of the division of pericyclane cells, the top of the side root merysystem is formed, which ensures their growth.
Thus, the conductive lateral root system is immediately associated with the conductive mother-root system and can receive substances from it necessary for growth, and in the future to transmit water and mineral salts to it.
The main functions of the root are fixing in the soil of the plant and the absorption of water. Sometimes roots are performed by other, not typical functions. In this regard, they have an atypical structure, in other words, for such roots are characterized by modifications, or metamorphosis (from Greek. Metamorphosis - transformation).
Roots
Roots are distinguished by the presence of a large number of spare tissue. They are usually formed in two-year-old plants in the first year of life. For the second year, flowers, fruits, seeds are formed. Thus, the root plant allows the plant to transfer rest period and complete development for the next year.
Korneflood - the name conditional. It is not related to the fruits, since it is not formed from a flower, but from vegetative organs - stem and root.
The ratio of the stem and the root in the formation of rootepodes is different, for example, in carrots almost all the root crust is formed by the root, and the turnp is stem.
Modern rooted roots are artificially derived. They play an important role in its nutrition, as well as in feeding animals.
Root cones
If the root root is a thickened main root, the root bumps are strongly thickened apparent and side roots. For them, as for rootepodes, a developed inquiring parenchyma is characterized. Root cones form appling kidneys, therefore are organs of vegetative reproduction.
Top 4 Articleswho read with this
Air roots are found in many tropical epiphytes (plants using trees as a support).

Fig. 1. Air roots.
Such roots are fluent in the air and absorb moisture in the form of rain and dew.
This type of modified roots is also found in the tropics. It is characteristic of trees growing on the ocean wetlands. The root system of such plants is complex and has aeronautic fabric Aerpenshim. Through the holes, the air falls into the Aerrenakhim and then passes into remote underwater areas of the plant.

Fig. 2. Respiratory roots.
Walker roots
Crested roots, or roots, are formed in plants growing at the husky orstive soil. They distribute the mass of the plant to the area enlarged during their account.
Pillar roots
The feature of the pillars roots is that they are laid on the branches. They are characterized by such roots of escapes for Banyan.
Banyan is not the name of the plant. This is the name of the growth features of some ficuses. You can call a banyan any tree with a volume crown, based on pillars-like roots.

Fig. 3. Indian Banyan.
Mikoriza
Mycorrise is symbiosis of roots and mushrooms. It is the roots with the gifs of the mushroom penetrated them. The cohabitation with the mushroom has a number of health benefits:
What did we know?
From the article on biology (grade 6), we learned that many plants root perform, in addition to major, some additional functions, with which the corresponding radiation modifications are associated. Although these functions are considered additional and specific, they are still related to the support and nutrition of the plant. Types of modified roots are very diverse.
Test on the topic
Report assessment
Average rating: 3.9. Total ratings received: 414.
Roots, in addition to their basic functions, often perform other functions. At the same time there are so-called metamorphoses of roots. Metamorphosis - These are evolutionary modifications of the form and structure of organs.
Consider them in more detail.
1. Symbiosis of roots with soil mushrooms.
Phenomenon symbiosis The roots of higher plants with soil mushrooms are widespread in nature.
The endings of the roots can be either braided with surfaces of mushrooms, or gifs mushrooms can be contained in the root core. This phenomenon is called mikodism , literal translation - " mribocornia ". Mikoriza can be an outer (ectotrophic), internal (endotrophic) or externally internal.
Etotrofny (outer) minecorosis can replace the plant root hairs. At the same time, root hairs often simply do not develop. Outdoor and outer-ended mycorrhosis occurs in wood and shrub plants (for example, birch, maple, oak, hazel, etc.).
|
Internal mycorrise is often found in various types of grassy and woody plants (for example, it is most species of cereals, onions, walnuts, grapes, etc.). There are such types of families that cannot exist without mitride (heather, pierce and orchid).

What are the symbiotic relationship between autotrophic plants and mushrooms manifest? Auto-flow plants supply mushroom symbiounds available to soluble carbohydrates. Mushroom symbiount, in turn, provides a plant with important minerals. For example, nitrogen-intimating mushroom symbiounta supplies a plant with nitrogen compounds, ferments and brings to glucose is difficult soluble spare nutrients. Excess glucose increases the suction activity of the roots.
2. Symbiosis of roots with bacteria.
In addition to mycorrhiza ( mikosimbiotrophy ), which is often found in nature, there is another symbiosis, which is not as wide as the first. This is the symbiosis of the roots of the plant with bacteria ( bacteriosimbiotrophy ).
Most often in legume plants, but sometimes some other plants are formed on the roots parenchymal thighs who are still called tubes . Inside these nodules there are many nodule bacteria. The peculiarity of these bacteria is that they can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the form of compounds that are absorbed by plants. For example, bean clover and alfalfa can accumulate 150-300 kg / hectares of nitrogen in their nitrogen. Therefore, in agriculture, legumes are often planted in order to enrich the soil with nitrogen.

3. Purchase roots.
In the roots of any plants, as a rule, in some quantities, spare nutrients such as sugar, starch, inulin, etc. are postponed. But there are cases where this inventory function is hypertrophilized and enters the fore. The roots are thicken and become meaty.
Such modified rod roots, which perform the function of the stock name called " rootfields " Most often, such a structure is found in twilight. For example, it is carrots, beets, turnips, radishes, etc. In the formation of these roots, part of the stem - hypocotyl (or stepper knee) participates in the formation of these root.

Roots in the picture: 1 - trouser; 2 - Swarms of Egyptian; 3 - Mammut varieties; 4 - carrots; C - Semilyoli; GP - hypocotyl; GK - Main root.
In some species of plants there are so-called root cones, which are highly thickened apparent roots. This, for example, Georgina, Labor, Church, etc. There are numerous transitions between root cones and "root crops".

4. Retracting or contractile roots.
There are some types of plants in which the root is sharply reduced in the longitudinal direction at its foundation. For example, this occurs in bulbous plants.
Covered plants often meet root roots
that provide dense fit to the ground of sockets (dandelion, plantain, etc.).
Thanks to the underground position of the root neck and vertical rhizome, the downturn of tubers in the soil. Those. Rafting roots make it possible to choose the most favorable depth of the occurrence in the soil. In adverse climatic conditions, for example, in the Arctic, the retractor roots help to survive a difficult winter flowering kidney kidney and renewal kidney.
Many tropical plants epiphytes have air roots . For example, such roots are found in plants of the family of orchid, arones and bromels. These plants have, so-called Aerrenhima. This is a special loose aircraft fabric from thin-walled parenchymal cells, from which jumpers are formed between large air cavities. Thanks to Aerrenhima, these plants are able to absorb the atmospheric moisture.

In the tropics on the marshy soils, trees are often formed respiratory roots or pneumatophores. These respiratory roots rise up (pay attention - this is negative geotropism!) Above the surface of a wetland soil to supply underground organs of plants through the hole system.

In mangroves, growing in the tidal lane of the tropical seas, there are trees with the so-called walled roots . These apparent roots are strongly branched and grow down, thanks to which the trees will retain stability on the primer.

The most interesting and spectacular wrecks can be attributed root backpoints Powerful branches of Banyan Fikus. Numerous supplied roots Bianan also grow down, as can be seen in the figure. Below they are very thickened, rooted, while developing their own root system. As a result, one single tree of Banyan can grow into a whole "grove", and at the same time the area is up to 500 m 2.
Reference blood roots Often found in large trees of tropical rain forest. In my opinion, they are no less interesting than wobble roots. The trunks of the trees of the first tier of the rain forest can reach giant sizes, with the root system they have surface. These giants must be kept in the soil (which is practically no) during frequent storms and shower. And the roots of the usual structure would never be able to whine such plants in such conditions. Therefore, there are special vertical grows in such trees on the roots of the soil surfaces. These growing boards are adjacent to the tree trunk. At the first stage, the random roots in their cross section of the rounded, but then gradually there is a strong one-sided secondary growth. The height of such shell roots in a tropical rain forest can easily exceed human growth.

8. Root trains.
Podid root trains Often found on the stems of various Cornezing Lian. To such, for example, applies ivy. The endings of these roots-clothespins are thickly covered with suction hairs that distinguish the mucus. Thanks to this mucus, they are very firmly glued to their support. Root-trailers are firmly held by plants, penetrating into various irregularities or cracks, walls, rocks, or some other support.

Ivy - roots


Plant organs other than the mains can also perform some other functions. Often, in such cases, modified organs are formed. Consider first of all the modifications of shoots (Fig. 1).
The meaning of modified escapes

modified underground shoots
Rhizome (drinking, sick, ferns) - underground escape with scratched leaves, covering styling kidneys (Fig. 1). The top kidney provides rising growth, and the stubby is its branching. And those and others can give the beginning of overhead leaves and shoots.
Tubers (Potatoes, Topinambur)- growing at the end of a long underground escape calledcolumn. There are usually no stubby kidneys on the column, and they form the so-calledeyesFrom which new plants may continue to develop. The main function of the tuber is the supply of nutrients (starch, etc.) (Fig. 1).
Bulb(onions, tulip) - underground escape with shortened stem and juicy leaves for the reserve of water and nutrients (Fig. 1). The base of the bulbs - damec - It is a flattened stem. From him in the middle of the leaves, called juicy scales. Nutrients are inhibited in them. In the center of the Donets there is a top kidney, and in the sinuses scales - stubborn kidneys. They can give the beginning of the above-ground organs or new plants. Outside the bulw is covered with dry scales, also representing modified leaves (onions, lilies, hyacinths).
Corm (Gladiolus) - Ombreted stem, outside covered with dry scales (gladiolus). Function: Nutrient stock (Fig. 1).
Modified overhead shoots
Adjusting to the conditions of the medium, the plants are modified by terrestrial shoots. Often modifications are not a whole escape, but one of its organs.
Fillocladium (Ilitian, Asparagus) - flattened sheet stems that perform the function of photosynthesis. Often such stems completely replace the leaves. In this regard, the cells of the outer layers of the cortex, which are directly under the transparent epidermum, are green, as they contain chloroplasts. Filloclands differ from the leaves by the presence of kidney on them, and sometimes even flowers and fruits (Fig. 4).
Spinys (hawthorn) and mustache(Grapes) - modified side shoots (Fig. 6). They are formed in the top of the sheet, and if the sheet dies away - above the leaf scar.
Mustache(Strawberry) - Long creeping shoots without leaves, which serve for vegetative reproduction (Fig. 1).
The modified shoots are also:
bud - relevant vegetative or generative escape;
kochan - severe kidney;
flower - shortened generative escape with limited growth, intended for seed reproduction of plants;
cone- A modified shortened coniferous escape, intended for seed reproduction of plants.
Modifying leaves
Often there are modifies of leaves.
The value of modified leaves

Sheet spines serve to protect the plant from either mechanical damage to animals. Such spines at Barbaris are modified weathered veins of the former sheet plate. White acacia and caragans, pair barbs are formed at the site of horses and are located at the base of the leaves.
At the schoom cactus, in addition to the hard "classic" barns, there are small briggble spines - glochidiawhich are easily separated from escape and cause painful sensations (Fig. 12).
Cacti barbs are modified renal scales that serve primarily to reduce transpiration (evaporation of water with leaves) in the arid conditions. But besides acute spikes, the leaves of cacti can be modified into camp "hairs" entangling all the plant. The main function is the protection of cactus from direct sunlight and dew collection (Fig. 13). Most often, the spines are deprived of chloroplasts and are not capable of photosynthesize.


Fig. 12 Fig. 13
Mustache Sheet origin is characteristic of representatives of the legume family. The main function is fixing the plant on the support.
In some cases, the leaves take the spare feature. In this case, the growth of the mesophyll occurs, its internal layers do not receive light and not photosynthesize, but nutrients or water (seats are thick) (Fig. 14) can accumulate in them.
Leaf origin have juicy sparkling schellowi Lilywich bulbs (Fig. 1).

Tropical Lian Dyshidia has unusual basching leavesFormed when the edges of the leaf plate edges. Leaves serve to storing rainwater. Through the upper hole in the sheet, not only water, but also the apparent roots of the lianas, absorbing water (Fig. 9, 10).
channel modifications
Channel modifications are often caused by the strengthening of one major functions. In contrast to the tubers of stem origin, they do not have a kidney.
The meaning of the modified roots
Flooring function (root, root tubers (root cones)).
Roots (carrots, turnips, beet) - the growth of the upper part of the root, into which the lower part of the stem or the entire shortened escape is dragged (Fig. 15).

Root tubers, or root cones, (dahlian, batt) - the growth of the side roots (Fig. 16).

Air roots of epiphytic plants (Fig. 17) are used to absorb air moisture, since they do not have the ability to obtain nutrients from the soil.

Orchids have such roots covered with several layers of dead cells forming a spongy surface. Such roots can absorb water during rain and dew, as well as absorb it from air in the form of water vapor. While in light, their cells often contain chloroplasts and take on the function of photosynthesis.
Reference roots, or roots-stuff,(Banyan, Corn (Fig. 18)) - Pressure roots in a number of large trees in the tropics are formed on the side branches high above the ground. They maintain heavy side branches, and also serve them with a source of mineral nutrition.


Fig. 18 Fig. nineteen
Respiratory roots - These are the side roots that grow not down, as it should be rooted, and up (Fig. 19). They are formed on wetlands, where the roots for normal functioning often lack oxygen. Reaching an uneplicable surface, they form at the ends open into the air holes. Inside such roots, air-capable parenchyma is formed with large interclausers connected along the entire length of the root. Oxygen diffuses on them deep into the root system, providing roots with the capabilities to obtain a sufficient amount of energy.
