Dame of bulbs. Overhead and underground sections of shoots Which parts of escape has a bulb
Seeds of plants usually germinate, hitting the ground at some depth. The very first escape, growing from the bud of the embryo, should break through the soil. On this underground part of the stem usually grow the first apparent roots. They can draw the base of the stem in the soil even deeper than it was immersed initially. Unlike rhizomes and tubers, the bulbs are well developed by the leaves, and the stem is very short and flat. He is called "Donets".
At the top of the Donets under the cover of the scales there is a kidney, from which the above-ground escape grows. From the stubble kidneys located below the top, new "subsidiaries" of the bulbs are formed. From each daughter Lukovitsa - "Baby" can grow a new plant.
What to do. Consider external structure bulbs.
- What is covered with a bulb with the outside?
- What does it matter?
What to do. Conduct the flange knife along.
What to watch. Consider closely pressed juicy scales - leaves.
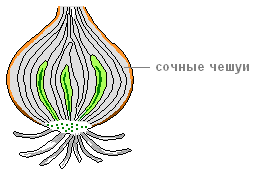
What is the difference between the internal scales from the outer?
What to do. Find and consider the stem dont, the top and side kidneys.

What to do. Consider the roots growing from the Donets.

- What are these roots?
- What root system do they form?
Prepare for a report. Draw a longitudinal incision of the bulbs and sign it part. Write down the signs showing that the bulb is escape.
Question 1. What kind of modified underground shoots do you know? Name plants having rhizome, tuber, bulb.
Tubers are formed as terminal thickening of underground shoots - collines. Strokes are growing from the base of the aboveground stems. Tubers develop as a result of thickening of the top kidney kidney (potatoes, hooker, earthwood pear). They are located kidney groups that are called eyes. Tubers serve for vegetative reproduction.
The bulb is an underground shortened modified escape. The bulb stem forms a don. Leaves, or scales are attached to the Don. Exterior scales are usually dry, they perform a protective function. They cover the compound scales, in which nutrients and water are laid. At the bottom there is a top kidney, which develops overhead leaves and a color-based arrow. At the bottom of the Donets develop additive roots. The bulbs are characteristic of perennial plants (lilies, tulips, bows, garlic, daffodils, wild onions, etc.). With the help of bulbs, plants can grow vegetatively.
Rhizome is also underground escape, outwardly similar to the root. Rhizome carries the scratched leaves, in the sinuses of which are stubborn kidneys. Pressure roots are formed on the rhizer, and side buses of rhizomes and above-ground shoots are developing from the sinus kidneys. Rhizomes are found in perennial herbatous plants (horsetails, ferns, nettle, valley, cereals, etc.). Rhizome is the organ of vegetative reproduction.
Question 2. How to distinguish rhizome from the root?
By appearance Rhizome is reminiscent of the root, but differs from it the presence of crystal leaves, leaf traces (scars from fallen leaves), kidneys, as well as the lack of root case.
Question 3. How does the potato tuber develop?
From the leaf of potatoes through the stalks to underground shoots (collisions), organic substances constantly express and are deposited in the form of starch. The tops of the columns grow, thicken and turn into large tubers by autumn.
Question 4. Why does the potato tube should be considered escape?
The potato tuber should be considered escape because it, like the escape, is formed by a stem that performs a sparkling function, has a kidney (eyes) and scratched leaves.
Question 5. What building has a bulb?
In the lower part of the bulbs, such as the onions, there is almost a flat stem-dona. Applying roots and modified leaves (scales) are departed from the Donets. External leaves - scales - dry and leathery, they perform a protective function; Internal - fleshy and juicy, nutrients are laid in them. In the sinuses of scales there are stubborn kidneys.
Question 6. How to prove that rhizome and bulb are modified shoots?
Externally, rhizome is reminiscent of the root, but he, like ground escape, there are uphety and stubborn kidneys, as well as film scales - modified leaves. Thus, the rhizoma has a stem (axial part of the rhizomes, kidneys and leaves (film scales), i.e., what is characteristic of escape. At the bulb we can also see all parts of the escape: Stem (Lukovitsy Donets), leaves (dry and juicy scales) and kidneys (between scales). This confirms that rhizome and bulb are modified shoots.
Question 7. What overhead modifications Escapes Do you know?
Surveys include spines (wild apple tree, wild pear), antenna (pumpkin, grapes), lets (bounds, luggage), overhead collisions, or mustache - (strawberries), stem cacti.
Donets Lukovitsa flusted into the plate axis of a shortened escape, which, together with meat-thickened leaves, it forms a bulb.
Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron. - S.-PB.: Brockhauses-Efron. 1890-1907 .
Watch what is the "Lukovitsy Donets" in other dictionaries:
Lukovitsa Luke Luke (Allium Cepa) L. Botanical Illustration from the Book of Martin Chilenshek (Slovensk. Martin Cilenšek) Naše Škodljive Rastline, 1892 Bulb (Lat. Búlbus) modified, usually underground plants escape with thickened short ... ... Wikipedia
damec - shortened and thickened stem bulbs, clubnelaukovitsa ... Anatomy and morphology of plants
Damec - the stem base of the bulbs, usually a disc-like or cone-shaped form, with strongly shortened interstices and modified leaves ... Dictionary of Botanical Terms
The subfamily of the Lily (Lilioideae) is 10 genera (approximately 470 species) belonging to 4 tribams. Representatives of the subfamily are found only in the northern hemisphere. The bulbs they have drawn up lower scales, as basal ... ... Biological encyclopedia
- ... Wikipedia
Squill - Urgenia Maritima L. Filler family Perennial Powerful bulbous plant, a lightless flower arrow of which reaches a height of 100 150 cm. The roots are basic, depart from the bluing dons, thick and durable, with thin side branching ... Encyclopedia of medicinal plants
Probably everyone knows such decorative plantsAs the kavern, or Iris (IRIS, Table 23, 24), a dress, or gladiolus (Gladiolus, Table 26, 3), and saffron, or crocus (Crocus, Table 25) ... Biological encyclopedia
Liliaguish ... Wikipedia
Bulb of flowering plant - The bulb is a modified escape. The bulb's dont is a strongly shortened stem, scales with modified leaves. Around the Donets are the roots of the roots, developing when boarding the bulbs in the ground. At the very Donets inside the bulb ... ... Official terminology
Shaying rot - See shake rot. The disease caused by fungus. Near the cervix appears gray depressed spots, which are further applied to the scales and the diacon of the bulbs. Mushroom persists on the bulbs, in the soil and on plant residues before… … Encyclopedia seeds. Vegetable crops
Common modifications of escapes covered plants They are rhizomes, bulbs and tubers. Usually they are formed in perennial herbaceous plants as organs in which spare nutrients are deposited. In such plants, green overhead units die for the winter, however, modified shoots remain in the soil. In the expense of the nutrients contained in them in plants, ordinary overhead shoots are developing again.
In addition to the supply of nutrients, the modified shoots perform another function. With their help, the plant can breed vegetatively.
Rhizome
Modified escape rhizome Many perennial plants are found (nettle, lily of the valley, dusty, etc.). Rhizome is B. upper layers Soil, reminds the root, but it turns horizontally.
Rhizome is escape, as it has the top and stubby kidneys, as well as the leaves that are modified in scales. The similarity with the root of Kornvik is attached to the apparent roots, which grow from it along the entire length.
For the growing season, the plant in the rhizome is postponed spare nutrients. Behind their bill, new young shoots grow from the kidneys.
With the help of root parts containing kidneys and roots, possibly vegetative reproduction Plants.
Bulb
Modified escape bulb Characterized for onions, tulip, lilies and other plants. At the bottom of the bulb there is a bleached stem called donets. From the diagram grow modified in scales of leaves of two types. The outer leaves are changed in dry scales that perform a protective function. Internal thick and juicy scales contain spare nutrients (in bulbs among other substances contain many different sugars) and water. At the bulbs from the Donets also grow kidneys.

In favorable conditions, pressing roots are growing from the bottom of the bulbs, as a result of which the urine root system is formed. From the kidneys can grow escape, but they can also develop in the so-called luki-kids. Each such bulb may give the beginning of a separate new plant. Thus, vegetative reproduction is carried out with bulbs.
Tuber
Modified escape tuber You can observe such plants as potatoes and Topinambur, as well as some others.
The tuber is formed at the top of another modified escape - stone. Strokes grow from the lower parts of the above-ground shoots and go into the soil. Organic substances synthesized by green parts of the plant in the process of photosynthesis are moved along the columns in their tops, and thus the tubers are formed here. In the tubers accumulate a lot of starch.
The tuber is at least a modified, but escape. It has short, but stroked in the thickness of interstices and many kidneys that are called eyes. Leaves have tubers reduced. The eyes are in the ducts of the tuber, and there may be several kidney glances in each such deepening.

That part of the tuber, which is connected to the column, is called the base of the tuber. From the opposite side of the base is the top of the tuber. The eyes are more closer to the top. Most often, the tops of the kidney develops into a young green escape.
Not necessarily be a botany to understand biological features vegetable crops. Knowledge in this area will help you to cultivate a bowstone correctly, without making elementary errors. Having at least a minimal idea of \u200b\u200bthe structure of the plant and its features, the gardener will be able to pay attention to the nuances that will increase the harvest. Since Luke's fruit is a bulb, a modified root process, then to increase productivity, first of all, it is necessary to learn more about the root system of this species.
Characteristic
Onions are a two-year culture related to the class of monocoons. The birthday of onion is Afghanistan, Iraq and Turkmenistan, with a mountain climate characteristic of these regions (reduced pressure and air humidity, solid rock rocks and minerals, but devoid of soil organic matter). Later by breeders, many varieties adapted for different climatic conditions were displayed.
For a family of onion, there is no clear distinction between the authorities. These plants are not divided into root, escape, leaves. The reason for this is a gradual transition from one morphological part to another. Rhizome, converted to the bulb, gives the beginning of a run that has no main stem, and is represented by a bunch of solid upright leaves. Grow onions for obtaining:
- Sevka - in order to obtain further planting material. Usually, .
- Directly onions, whose varieties are described in.
- For decorative purposes. The varieties and methods of growing decorative bow are described.
The generative bodies capable of sexual reproduction are matured only for the second year of growth.
Root system of different types of onions
Like the entire class of single-bedroom, the onions has a basic root system. That is, the plant does not have the main root, and instead there are many apparent thin threads-roots. This allows Luke to firmly strengthen in the soil: the roots are gradually drawn into the bulb inland, the ground is penetrated with a dense network, cling to the rhizomes of other plants.

Onions has a basic root system
Onions are still considered to be superficial, siding shallow culture. For this reason, there are special loose types of soil for it, especially when seeds are planted.
Roots of the bow have a high ability to chemotropism - instinctive search and absorb dissolved nutrients. The roots are annual structure and die after the end of the growing season. Nutrients accumulate in a modified prickene shoot - a bulb.
Structure of stem
The stalk of the onion bows is also modified. It is represented in the form of a simplified plate - the Donets. On this plate there is one or more kidneys surrounded by the leaves of the vaginal type. The kidneys are called the buddies.
In the reproduction of a vegetative way, the plant forms a "heel" - dead and harmonious remnants of the maternal donta. The heel protects the bulb against excessive moisture penetration and subsequent rotting, which is especially important in the last stages of its development. Therefore, to ensure good crop forthstream, it is more profitable for its spit.

Onion in the section
The capacity of the plant depends on the incidents of the plant to bring the crop of greenery (the less adventures, the more actively the leaves are developing).
The structure of leaves
For the onion onions are characterized by shuddy meat, the leaves of the cone-shaped shape, shutting up to the end and hollow inside. From frosts and lack of moisture sheet protected by a loose wax. The color of the leaves depends on the level of illumination: the more sunlight gets a plant light color Feather. In general, the color varies from light-salad to the SIZO-GREEN, DARK.
Leaves also differ in size and density. Closer to the completion of the growing season, the leaves are compacted, pronounced pronounced housing (in the onion it is longitudinal transverse). The most dense are the leaves that have formed from the extreme open scales of the bulbs. At Luka Multi-tier differs the root system with which you can familiarize yourself.

A cone-shaped bite onion leaves, causing to an end and hollow inside.
Lukovitsa structure
The bulb is called seating right on the bottom of false leaves, protecting inside the kidney. The transverse section shows that the flakes form concentric circles, and their density and juiciness increase when approaching the center. Forming scales are divided into:
- closed juicy. The modified leaves of cone-shaped form, non-assimilant and performing an exceptionally sparkling function.
- open juicy. Thickened, not capable of photosynthesis of a piece of a sheet with a lush base, thinning to the top.
- chesows dry cover. They have a different color (depending on the variety -,), dense and smooth, protect the bulb from pests, drying and helps it is stored for a longer time.
Juicy pieces of bulbs depending on the variety can have loose grainy, fibrous, paper, mesh or film structure.
In the center of the bulbs spirally arranged kidneys, of which heterophytes (colorless shoots) or new bulbs are formed in the future . In terms of the number of such kidneys, adequateness and the nest of the bow are determined.
On the shape of the bulbs are divided into several main species:
- flat;
- round-flat;
- rounded;
- long (elongated or oblong);
- mellic;
- round-melon.
Flower and escape structure
The number and dimensions of the color-point shoots from the onion flashes depend on the variety and conditions of cultivation . They are formed after new feathers cease to grow, at the very end of the growing season. For this reason, escape has the ability to photosynthesis, which ensures the ripening of seeds. Seeds also participate in the landing. They are obtained, as a rule, segue. Growing onion B. open soil Seeds and sugrees are described.
Called bowls of onion plants with an arrow, and the process of their formation is short. The arrow is a hollow inside a thin-walled tube having a small thickening at the base. It can reach it from 45 to 130 cm.
Luke flowers can have a white, blue, purple or yellowish color. They form a complex inflorescence-umbrella, in which it can be from several pieces to several thousand flowers. On average, the flowering period of a separate flower is 3-7 days, and the total umbrella is 7-35 days. The flowers of the symmetric shape do not have cups, but they have a permanent set of gamemarketophytes - 6 stamens and 1 pestle.
Reproduction
For onion, both sexual reproduction with seeds, and vegetative with bulbs are characteristic. Sexual reproduction occurs by self-pollination or pollination by insects. During the double fertilization, one seed is formed on each flower. A dry multifreeze fruit is developing from the colorful. The aging of the seed of the wrong pyramidal shape occurs within 40-60 days. After the seeds covered with dense black leather (for which they were called "Chernushka" in the people), ready to assemble . In 1 gram, up to 1000 individual seeds are usually fond. 
Under adverse conditions, life processes are freezing, the active formation of adventures and the accumulation of nutrients in the bulbs begins.
In this form, the plant is experiencing a difficult period, and with the onset of heat gives several shooters and the bulbs at the second stage of development does not forms.
Features landing
Considering such a structure of the plant, it can be assumed how and where the bow should be planted. The most profitable is the creation of suits, while the lows are buried shallow in loose plenty of powerful soil . Eastern varieties You can soak in the ink, grooves up to 1 cm deep. It is necessary to plant in a well-lit place, avoid dimming and excess moisture.
The disembarkation falls at the end of April, when the soil is well a fundamental and the longest day day.
Video
conclusions
The structure of the onion bow allows him to easily experience an unfavorable period, but this will noticeably reduce its yield. Maintaining normal conditions is a pledge of abundant fruiting, good layers of bulbs. Knowing the stages of the development of onion can be installed the cultivation mode of it as a two-year-old culture, which will noticeably increase its productivity. How to store onions at home is described on this.